Garmin, the maker of fitness trackers, smartwatches and GPS-based wearable devices, is currently dealing with a massive worldwide service interruption after getting hit by a targeted ransomware attack, an employee of the company told The News on condition of anonymity.
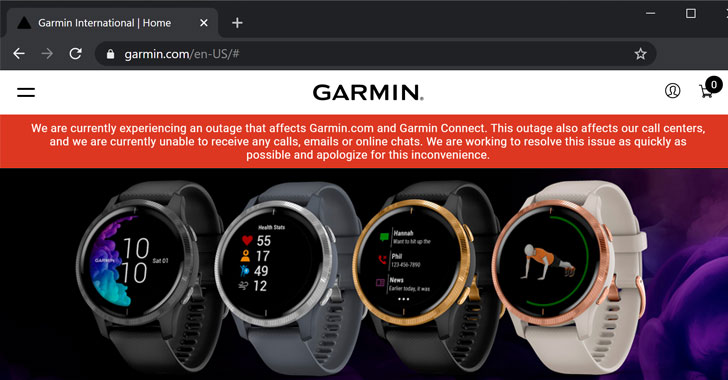
The company's website and the Twitter account say, "We are currently experiencing an outage that affects Garmin.com and Garmin Connect."
"This outage also affects our call centers, and we are currently unable to receive any calls, emails or online chats. We are working to resolve this issue as quickly as possible and apologize for this inconvenience."
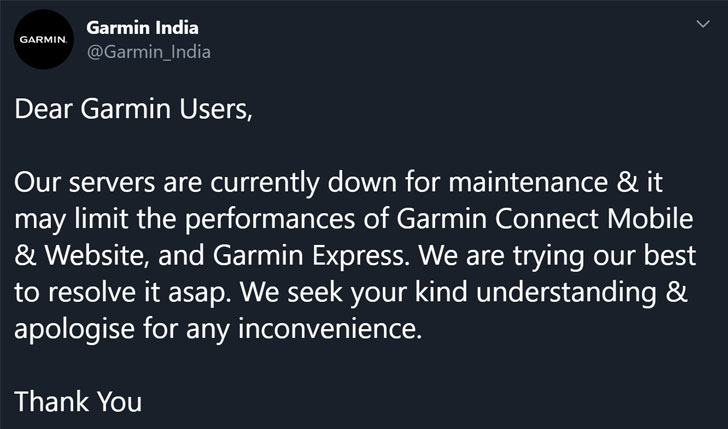
As a result, the company yesterday was forced to temporarily shut down some of its connected services, including Garmin Express, Garmin Connect mobile, and the website—restricting millions of its users from accessing the cloud services or even syncing their watches locally to the app.
Though not much information is available on technicalities of the cyber attack, some local media reports claim hackers have managed to compromise the company's application and database servers with ransomware.
It also says Garmin has sent announcements to its IT staff in Taiwan-based factories announcing the next two days of planned maintenance, i.e., July 24 and 25.
Multiple sources in the cybersecurity community suggest that the cyberattack may have involved WastedLocker, one of the targeted ransomware gang, known as the Evil Corp or Dridex.
The modus operandi of the attackers behind WastedLocker involves compromising corporate networks, performing privilege escalation, and then using lateral movement to install ransomware on valuable systems before demanding millions of dollars in ransom payment.
According to experts at SentinelOne, WastedLocker is a relatively new ransomware family active for the last few months and has since been attacking high-value targets across numerous industries.
WastedLocker uses JavaScript-based SocGholish toolset to deliver payload by masquerading as system or software updates, exploits UAC bypass techniques to elevate privileges, and leverages Cobalt Strike for lateral movements.
"All the security technology in the world is not going to protect against determined attackers. 97% of losses stem from socially-engineered attacks and over 90% are initiated by email," Lucy Security CEO Colin Bastable shared a comment with The Hacker News.
"There are no front lines in cyberwarfare – we are all fair game for bad actors, and no entity or person is safe from cyber-attack. Train your people to detect and resist ransomware attacks – just as you patch systems, patch your people with regular, varied, continuous and well-planned security awareness training to make them part of your defenses," Bastable added.
Gurucul CEO Saryu Nayyar also suggested the same:
"You just don't know when the bad guys are going to attack and who will be their next victim. However, what we do know is every organization is susceptible to ransomware attacks."
"So, do what you can to prepare and respond. Hopefully, Garmin has a daily backup regimen for the company's systems and data. That's table stakes. If you get hit, at least you can recover your data."
Garmin has not yet officially confirmed whether the incident is a ransomware attack or not, but we have contacted the company and will update the story as soon as we receive more information on this incident.
"There are no front lines in cyberwarfare – we are all fair game for bad actors, and no entity or person is safe from cyber-attack. Train your people to detect and resist ransomware attacks – just as you patch systems, patch your people with regular, varied, continuous and well-planned security awareness training to make them part of your defenses," Bastable added.
Gurucul CEO Saryu Nayyar also suggested the same:
"You just don't know when the bad guys are going to attack and who will be their next victim. However, what we do know is every organization is susceptible to ransomware attacks."
"So, do what you can to prepare and respond. Hopefully, Garmin has a daily backup regimen for the company's systems and data. That's table stakes. If you get hit, at least you can recover your data."
Garmin has not yet officially confirmed whether the incident is a ransomware attack or not, but we have contacted the company and will update the story as soon as we receive more information on this incident.
Comments
Post a Comment